«Lotus effect»

In the 1990-s German botanist Wilhelm Barthlott studied the “lotus effect” – an effect of extremely low wettability and self-cleaning, which takes place due to the fact that water drops don’t linger on the leaves and petals of lotus, but slide down from them.
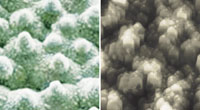
Surface relief of lotus leaves and petals is represented with ordered relief of micron and nanometric size, covered with thin waxen (hydrophobic) layer. Getting on this surface, a drop takes virtually ideal spherical shape and easily slides down from it, removing dust and dirt particles.
Synthesized hydrophobic nanorelief is an analogue of natural surface of lotus leaves
Modern technologies of colloidal particles synthesis with required properties and prearranged size have ensured to «Nanosintez» a breakthrough in creation of protective coatings of new generation.
Key concepts of protective coating technology:
- creation of required nanorelief on the treated base using modified nanoparticles;
- hydrofobisation of these particles, which provides the surface with superhydrophobic properties and self-cleaning effect;
- stabilization of coatings as a result of different polymer usage, which keeps particles on the surface.
When studying obtained coatings on atomic-force microscope, the nanorelief, formed on the treated material, appeared to be practically identical to the surface of lotus leaves. Thus, protective nanocoatings can reproduce “lotus effect” on any material surface.
Principle of mutual interaction of nanocoating and carrier
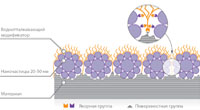 Creation of new generation protective coatings is based on so called “chemical inoculation method”: nanocoating is applied on surface of the material subject to protect from influence of aggressive agents of environment, and is bonded to it due to strong chemical bonds. Forming of a protective layer on the treated surface takes place by means of mutual interaction of active groups of material surface and anchor groups of protective nanocoating.
Creation of new generation protective coatings is based on so called “chemical inoculation method”: nanocoating is applied on surface of the material subject to protect from influence of aggressive agents of environment, and is bonded to it due to strong chemical bonds. Forming of a protective layer on the treated surface takes place by means of mutual interaction of active groups of material surface and anchor groups of protective nanocoating.

Such scheme works on every surface, giving hydrophobe and self-cleaningproperties to material. Treated item is resistant to different kinds of contamination, icing, and also has heat-insulated properties. Thus, protective nanocoating extends material lifetime, preserving its quality.
Unique nanocoating for each material
Each material is individual and has particular structure (glass, fabric, stone, wood etc.), which means specific active groups on its surface. When developing nanocoatings «Nanosintez» specialists take into account properties of the carrier (solid) and its surface layer, carefully select anchor groupings which will later interact with active groups of particular material, forming strong chemical bond.
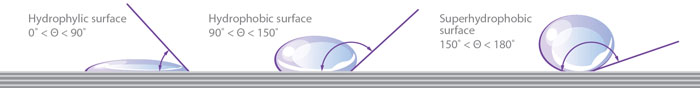
One of the main advantages of «Nanosintez» nanocoatings over other manufacturers is wetting angle
Wetting angle is an angle between the surface of material and the plane tangent to the surface of liquid. Lesser value of wetting angle shows larger drop spreading and, consequently, larger area of contact between water and material. Bigger wetting angle helps drop to take ideal spherical shape, as a result of which the area of its contact with hydrophobic surface is minimal and wetting is practically absent.
At the moment protective nanocoatings market is represented mostly by products which wetting angle is within 110°—120°. «Nanosintez» has developed coating with wetting angle over 150°.